Have you ever wondered if modern cruise ships have anchors and if so, where are they stored, and how big are they?
Modern cruise ships have what’s known as a stockless or patent anchor. This type of anchor is suitable for a wide range of different sea bed types, which cruise ships need as they travel through different waters and varying ports.
They are called stockless anchors because they don’t have a horizontal stock across the top of the shank.

Do Cruise Ships Have Anchors?
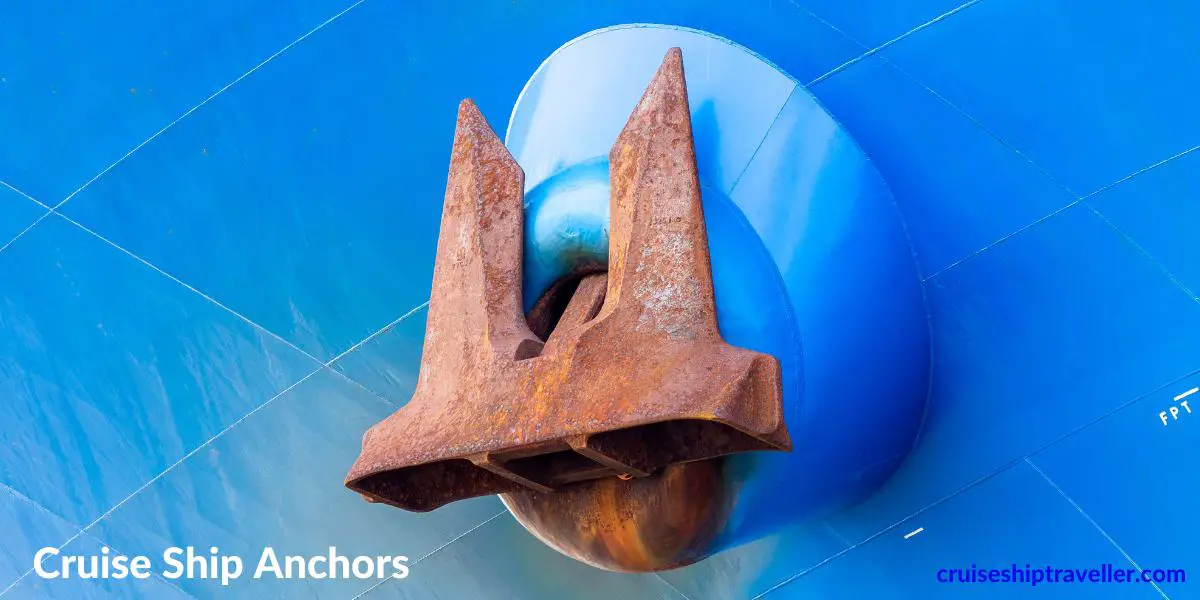
Like most ships, cruise ships have anchors. Anchors are required for holding a ship in place and preventing it from drifting due to winds and currents.
Anchors come in various shapes and sizes. Cruise ships have stockless anchors. This is a design of anchor that has particularly heavy flukes which are connected to a shank. These heavy flukes can dig into the seabed.
Do Cruise Ships Have More Than One Anchor?
Most cruise ships have two anchors, one port side and one starboard side at the front of the ship, although they are not often deployed at the same time.
One anchor is sufficient to keep a ship in position, although two can have their uses in specific circumstances.
Having two anchors means there’s always a backup should one ever be required. There is a lot of machinery and chain involved in the anchoring process and if any were to become damaged or required maintenance the other anchor could be used.
How Big Is A Cruise Ship Anchor?
Cruise ship anchors can be up 15ft to 20ft in height and 10ft to 15ft wide. Anchors are generally proportional to the size of the cruise ship. The larger and heavier the cruise ship, the larger the anchor can be expected to be.
The largest oasis-class Royal Caribbean cruise ships are some of the largest in-service ships sailing today and can be expected to have the largest anchors on any cruise ships.
The new Royal Caribbean icon-class cruise ships will be larger still and so will the anchors.
How Much Does A Cruise Ship Anchor Weigh?
Cruise ship anchors are somewhat proportional to the size of the ship. The larger the ship, the larger the anchor. A typical cruise ship anchor can weigh 10 to 15 U.S tonnes (9000 to 13600 kilos).
However, the weight of the chains is far heavier and much more of a factor in holding a ship’s position when it’s anchored offshore.
It’s the weight of the chain that holds the ship’s position, while the anchor acts to hold the end of the chain, preventing it from being pulled along the seafloor.
Ship Anchor Compared To Human
Cruise ship anchors can be 2 to 3 times an average human height of 5ft 9inches.
Assuming an average human weight of 80kg, an anchor weighing 10000 to 13500 kilos would be 125 to 168 times heavier.
In the photo below, you can see a human and cruise ship anchor comparison. Two maintenance workers underneath the anchor of Norwegian Cruise Line’s ship Norwegian Jewel, which was raised for maintenance.
In our post about the bottom of a cruise ship, we highlight a video clip of an anchor being freshly painted, and you can see it is about three times the height of the man doing the painting.
How Long Are Cruise Ship Anchor Chains?
The weight of anchor chains plays an important role in holding a cruise ship in position, much more so than the weight of the anchor itself.
When an anchor digs into the seabed, there must also be a sufficient length of anchor chain also lying on the sea bed. This provides extra weight and slack to the chain, which can absorb forces from the ship’s movement.
When a ship is properly anchored, the amount of anchor chain released should be 5 to 7 times longer than the depth of the water.
If the water depth was 50 ft (15m) the anchor chain released would need to be 250ft to 300ft (75m to 105m).
The anchor chain lies horizontally from the ship to the embedded anchor. Much of it is flat on the bed of the water.
The ship will not be sitting directly above the anchor but rather drawn away from it by wind and water currents.
Each individual link on the anchor chain weighs a considerable amount in its own right. This weight of the chain causes it to sag into a curved shape from the anchor chain on the sea bed up towards the ship. This is referred to as a catenary, a flexible hanging chain.
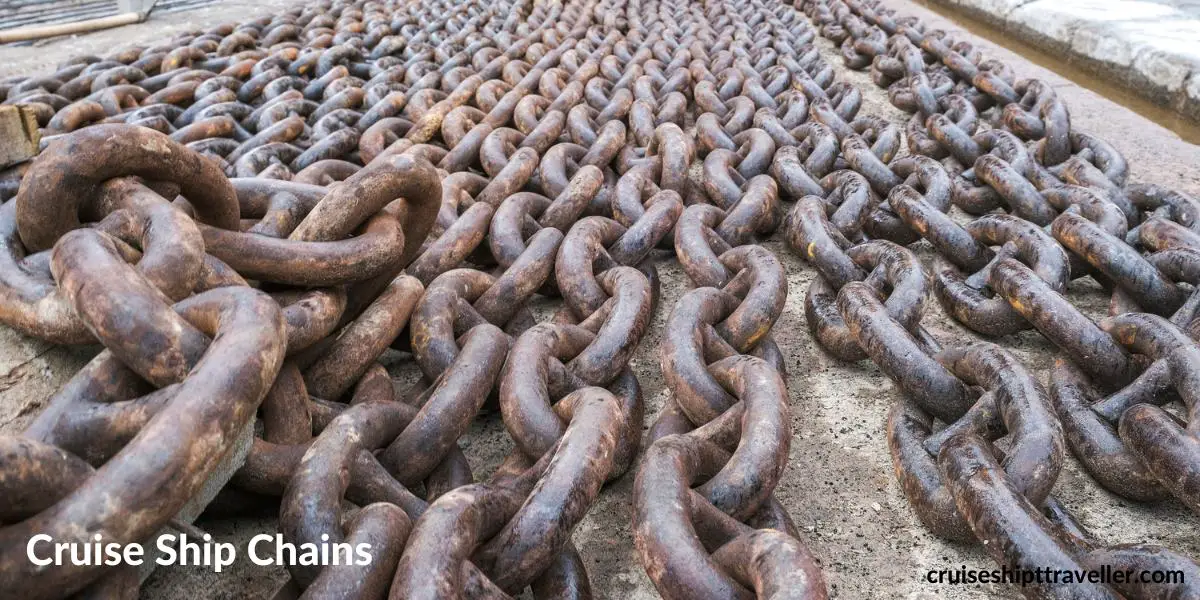

Markings on Anchor Chain
To indicate the length of the anchor chain released are markings on the actual chain, individual chain links of a different color, usually a red shackle, and white links on either side.
These markings indicate every 90ft (27.4m) of chain released.
The way it works is for every 90ft extra links, and either side of the red shackle will be painted white.
For example, a 360ft chain would be indicated with four links painted which either side of the red shackle (4 x 90ft = 360ft).
When do Cruise Ships Use Anchors?
If the draft of a cruise ship is too deep for a shallow port and waters, this prevents the cruise ship from docking. The cruise ship will have to anchor offshore in deeper waters, and passengers will have to be tendered to port.
Reasons a cruise ship might need to anchor include:
- Port waters too shallow
- Waiting to berth (park)
- Holding position during a storm
- Waiting for port channels to clear
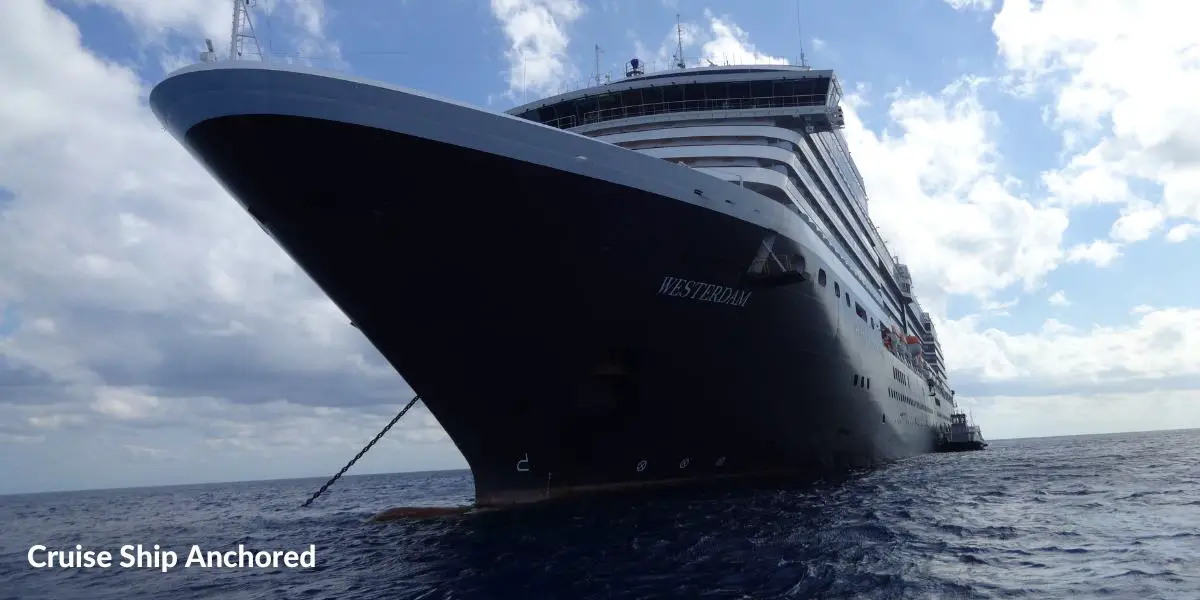

How Does A Ship Anchor Work
An anchor can be dropped in one of two ways.
- Engage in gear and walk back at desired pace or drop released for faster
- Release manual break for emergency release
The manual brake can be released in an emergency to release the anchor as quickly as possible.
When the anchor hits the seabed, the bridge crew will use the bow thrusters to maneuver the ship, causing the flukes of the anchor to dig in to the seabed.
With large cruise ships, it’s not so much the size and weight of the anchor that holds it in place, it’s more the total weight of the chain.
The anchor holds the end of the chain in position while much of the chain lays along the seabed before rising up to the cruise ship when forces such as wind are applied.
If there is no pull on the chain, and it’s slack, then there is no weight on the chain.
As the cruise ship moves, the chain’s slack changes when it’s slowly stretched and becomes taunter.
Depending on the stage of slack it will be referred to as:
- Lightweight
- Medium weight
- Heavyweight
At medium weight, the ship will have moved away from the anchor, and some of the chain will have been lifted from the seabed.
When the chain is deemed heavyweight, there is no slack in the chain. At this point, the anchor is acting to keep one end of the chain in position.
As a ship moves away from the anchor, the anchor chain gently extends as some chain is lifted from the seabed, absorbing some of the force that’s moving the ship. The force is not directly transferred to the anchor.
Whenever the forces subside, the chain slackens, and some of it falls back on the seabed as the ship eases back toward the anchor.
This is why anchor chains are so long. The longer the chain, the more force it can take before breaking the anchor free of the seabed.
If ships had short anchor chains that were just long enough for the anchor to bed down with a much shorter and tight chain, as soon as any excessive force is applied to moving the ship, it would be applied directly to the anchor, possibly causing it to break free.
Cruise Ship Dropping Anchor
To understand how a cruise ship works, we found this video which shows the Princess Cruise vessel, the Coral-class Island Princess cruise ship dropping an anchor.
To give you an idea of scale Island Princess is a mid-sized cruise ship, 91,627 gross tonnes with a capacity for 2200+ passengers and 900 crew.
Some of the biggest cruise ships are 2 to 2.5 times bigger, and the anchor and chains would be proportionally larger too.
Island Princess Dropping Anchor
The video shows:
- 0.40 – Anchor lowered to water level
- 1.05 – Port side windlass
- 2.05 – Anchor starts dropping
- 4.03 – Brought up to a port anchor of 5 and a quarter in the water.
Do Modern Cruise Ships Need Anchors?
While cruise ships, in theory, can use the dynamic position system that utilizes a combination of computer technology and GPS and to automatically control the propellors and bow thrusters, keeping the ship in the desired position by acting against the forces of the sea and winds.
Although this would involve keeping the ship’s engine running, using lots of fuel and keeping the crew busy overseeing it all.
An anchor is a much more efficient process, including much less fuel.
More importantly, a cruise ship can always use an anchor in the event of a loss of power, which, in some situations, could be vital.
Basic Anchor Terms:
- Anchor aweigh – means to take up the anchor from the waters bed
- Bed down – anchor on the seabed
- Bosun – operates the windlass and anchor
- Brought up -when the ship’s way has stopped and is riding to her anchor. There’s an equilibrium between the weight and forces on the ship and the weight of the anchor cable.
- Forecastle raised deck front part of the ship
- Flukes – projection of anchor that digs into the seabed
- Hawse pipe -where the anchor is stored
- Heave – a strong pull
- Rode – anchor chain
- Windlass – a type of winch used especially on ships to hoist anchors
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the largest anchor in the world?
The biggest anchor in the world belongs to the largest ship in service, Pioneering Spirit. The ship has a gross tonnage of 403,342 far greater than the next largest ships by gross tonnage.
One of the largest anchors in the world now on land is that of the Seawise Giant It is 36 tonnes and is on display at the Hong Kong Maritime Museum.
Why is Water Coming From A Ship Anchor?
When an anchor chain is lying on the seabed, it picks up all sorts of debris and mud, which must be cleaned to prevent the chains from seizing up.
The anchor chain is heaved up through the hawsepipe at the bow of the ship, while at the same clean, powerful jet sprays within the hawsepipe clean the anchor chain.
What Happens if an Anchor Gets Stuck?
If an anchor became stuck in the seabed, such as being caught on a rock, the cruise captain would try to maneuver the ship in various ways to try and break it free.
As a last resort, the anchor chains would have to be cut, leaving the anchor on the seabed. Rather than lose the anchor, a buoy could be attached to the last piece of the chain so it could be recovered later.
What Would Happen if a Cruise Ship Lost its Anchor?
There are usually two anchors on a cruise ship, one on the port side and one on the starboard side. If one was lost, the other could be used.
We have this post if you need ways to remember port and starboard side.
If all anchors were lost, the ship would have to use propulsion and bow thrusters to maintain position.
If power was also lost, the ship would be at the mercy of the forces of wind and waves, which would cause it to drift. In this instance, the captain would have to call for assistance.
Do Cruise Ship Anchors Touch The Ocean Floor?
Cruise ship anchors need to reach the floor of the seabed. More than that, they need to dig into the seabed to maintain a grip and have enough chain links to be laying on the seabed to absorb any weight-pulling forces.
Can a Cruise Ship Anchor in the Middle of the Ocean?
Cruise ships can only anchor in seas where the anchor can comfortably reach the bottom of the sea bed and still have enough chains left to lay on the seabed.
If the cruise chain is too taunt, any pressure moving the ship would put too much pressure on the anchor and possibly break it free from the seabed.
There are ocean depths that cruise ship anchors cannot reach. This is because they are primarily designed for anchoring in shallower coastal waters. Excess anchor rode is not on board because it takes up too much space and is rarely required.
If the anchor cannot reach the seabed, it is serving no purpose and is simply a weight dangling from the ship into the sea.
How Much Does A Cruise Ship Anchor Cost?
The cost of an anchor mostly depends on its size and weight.
There are also the logistics of transporting such a heavy item and the additional costs of installing the anchor.
As ship anchors are not commercially available for sale, it isn’t easy to estimate a price, but for a large cruise ship anchor on its own without a chain, it could be expected to cost a six-figure sum.